
Considering that regulation can be expressed as the management of complicated systems within the body, then modulation is the influence of control over that system of management which occurs as either a stimulatory or inhibitory effect.
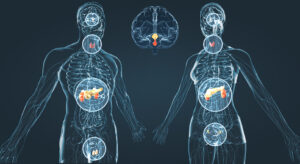
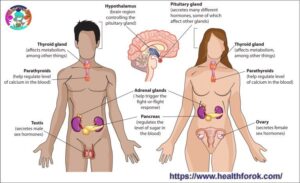
The Endocrine System.
Of all the many complicated interlinked systems in the body the endocrine system stands out as the prominent regulatory system involved in the management of homeostasis.
Consisting of a network of glands which produce the various hormones that regulate tissue function, growth and development, metabolism, sexual function, reproduction, sleep, mood and the list goes on. This system acts like a chemical messenger (signalling) system consisting of various feedback loops of each of the hormones released by the many internal glands.
Interfacing the endocrine system with the part of the brain responsible for its own regulation the hypothalamus, is the neuroendocrine system. The neuroendocrine system is a complex signalling system made up of neurons, neuroendocrine cells, hormones and glands relaying messages from the brain and the nervous system to the glands which respond by making and releasing hormones.
Homestasis.
Can be defined as a set point of balance within the systems responsible for proper functioning of the body. Various systems work to promote stability in the body by releasing stimulus when the hormone levels increase or decrease, a stimulus is generated which causes the cells to act accordingly to maintain proper functioning inducing a state of equilibrium. Homeostasis is controlled by three main processes osmoregulation [1], thermoregulation [2] and chemical regulation [3], with the systems that regulate these processes being mostly the nervous system, respiratory system, endocrine system, urinary system and the reproductive system. The endocrine system is directly involved in the regulation or control of these systems via the release of hormones which produce stimuli which produces changes in the system that lead to balance and proper system functioning.
ECS the grand modulator.
The Endogenous Cannabinoid System is a primary modulatory system in the function of brain, endocrine and immune tissues. It appears to impose a controlling influence over the regulation of the secretion of hormones related to reproductive functions and response to stress. The key components of this system are: endocannabinoid receptors types CB1 and CB2, their endogenous ligands (N-arachidonoylethanolamide, 2-arachidonoyl glycerol), enzymes involved in their synthesis and degradation, as well as cannabinoid antagonists.
In short the endo-cannabinoid system modulates the regulation of the neuroendocrine system, which serves to regulate organ function and stress response helping achieve and maintain a healthy balance.
Modulate anxiety, depression, OCD, or PTSD.
As a result of the endocannabinoid system being intricately involved in stabilizing bodily processes, as well as the regulation of many functions of the brain that tend to be affected after a traumatic experience, such as those responsible for anxiety, fear, memory and sleep, modulation of the ECS is an important aspect in achieving and maintaining balance.
Brain scans from a small study conducted in 2010 on the impact of cannabidiol (CBD) specifically on people suffering with social anxiety disorder demonstrated significant changes in blood flow to the regions of the brain linked to feelings of anxiety. Several studies [1], [2], [3], since then have shown promising results for CBD as a viable treatment for anxiety, with the most promising case study concluded in 2016 on a child with a history of trauma in which researchers found that cannabidiol reduced the child’s anxiety and helped her sleep.
Cannabinoids particularly CBD, have been shown to play a pivotal role in assisting PTSD by helping to supress the retrieval of the underlying trauma, effectively preventing traumatic memories and associated nightmares, whilst promoting emotional wellbeing, making it a popular treatment for PTSD patients.
In Conclusion.
Modulation of key systems in the body responsible for the regulation and maintenance of proper bodily function regulated by hormonal and chemical changes, plays an important role in respect to the positive influence it produces on the 3 key biological processes responsible for the promotion of homeostasis, namely osmoregulation, thermoregulation and chemical regulation. Therefore the ability to modulate our systems can promote stability and balance and assist us in alleviating many conditions arising from overactive or inadequate production of hormones responsible for the regulation of bodily processes, including anxiety, depression, OCD, or PTSD.